Source: AFP.
Source: AFP.
This International Women’s Day, the United Nations is celebrating under the theme “Invest in women: Accelerate progress”. Challenges that we are facing in the world today can only be addressed by solutions that empower women, which make up half of the world’s population. In particular, raising the female labour participation rate and ensuring that women receive adequate representation in leadership positions are two key avenues to closing the gender gap which will have beneficial effects on economic growth.
The current global labour force participation rate for women lags that of men, not because women are not productive, but because they are often informally employed in work that is economically unrecognised. Household and caregiving duties are examples of the work women do that is neither quantified nor captured by standard economic measures. Greater female labour participation is not only central to realising women’s rights, but also to growing economies and alleviating the gaps created by a shrinking working age population.
Within Asia, India is amongst the lowest ranked in terms of female labour force participation rates. Coupled with the fact that it has the largest population in the world, the country is well positioned to grow its economy rapidly in the near future, especially if it is able mobilise more of its female population to join the workforce. This will, however, be contingent on whether the necessary infrastructure to support women are put in place, such as access to affordable, quality childcare and overall safety. On the other end of the spectrum, while Japan has relatively high female labour force participation, the next step would be to improve the quality of that participation, and we see upcoming corporate governance reforms potentially uplifting more women leaders, boding well for improved organisational performance.
Invest in women: Accelerate progress
Women’s development has come a long way, from the 1848 New York Seneca Falls Convention – the first women’s rights convention organized by women – to eight countries electing or swearing in their first woman Head of State or Government in 2021. Yet the journey has been an uneven one, dotted with setbacks such as the Covid-19 pandemic and the overturning of abortion rights (Roe v. Wade) in the US.
It is hence befitting that this International Women’s Day, the United Nations is celebrating under the theme “Invest in women: Accelerate progress”, for challenges that we are facing in the world today can only be addressed by solutions that empower the women that make up half of the world’s population.
When more women work, economies grow
Besides the fact that women’s economic empowerment is central to realising women’s rights and gender equality, when more women work, economies grow. The working age population is also shrinking in most countries, and even for the few countries where it is not shrinking yet, growth rates are declining. Greater female labour participation in the labour force could help by improving the sustainability of public-funded pensions, and alleviate the gaps created by a declining cohort of working age people.
According to the International Monetary Fund (IMF), women’s economic empowerment boosts productivity, increases economic diversification and income equality in addition to other positive development outcomes1. For example, it has been estimated that increasing the female employment rates in OECD countries to match that of Sweden, could boost GDP by over USD 6 trillion2. Conversely, gender gaps could cost the economy ~15% of GDP3.
Which countries, then, have significant potential to grow their GDP by raising their low female labour participation rates? Do low female labour participation rates simply mean that women are just sitting back and relaxing? In the sections below we consider the above questions.
Women at home
Women account for half of the world’s population; yet, according to data provided from LinkedIn4, women accounted for only 41.9% of the workforce across 163 countries in 2023. Many women are informally employed in economically unrecognised work such as unpaid caregiving duties, the value of which is neither quantified nor captured by standard productivity measures like a country’s gross domestic product (GDP).
According to a 2014 study by the OECD Development Centre5, women around the world spend an average of three to six hours on unpaid care activities (i.e. unpaid services provided within a household for its members, such as caring for children and housework, which one could theoretically pay a third person to perform). This is disproportionately higher than the half-hour to two hours spent by men. The disparity could be due to ingrained gender roles, where unpaid care activities are often seen as women’s responsibilities.
This situation was exacerbated during the Covid-19 pandemic. Research commissioned by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation found that women disproportionately lost employment and had increased household care responsibilities, especially on the back of disrupted childcare services6.
The OECD estimates that unpaid work could contribute to ~15% of GDP on average across OECD countries, while the International Labor Organization (ILO) estimates that unpaid care and domestic work could be valued up to 10-39% of GDP7.
Women in the workforce
Empowering women to reach their full economic potential not only tangibly supports the key goal of reducing gender inequality, but also has tremendous significance on the advancement, competitiveness, and future-readiness of economies worldwide. In this regard, empirical evidence shows that women’s economic empowerment and the closing of gender gaps in key areas is associated with positive macroeconomic outcomes, including higher economic growth, lower inequality, increased productivity, better financial sector outcomes and greater financial stability.
– International Monetary Fund8
It follows, naturally, that the current global labour force participation rate for women is just above 47%, a whole 25 percentage points (ppt) lower than men at 72.5%9. Labour force participation rates are lower for women than for men across all regions globally and India is a notable laggard.
Exhibit 1: Labour force participation rate, female
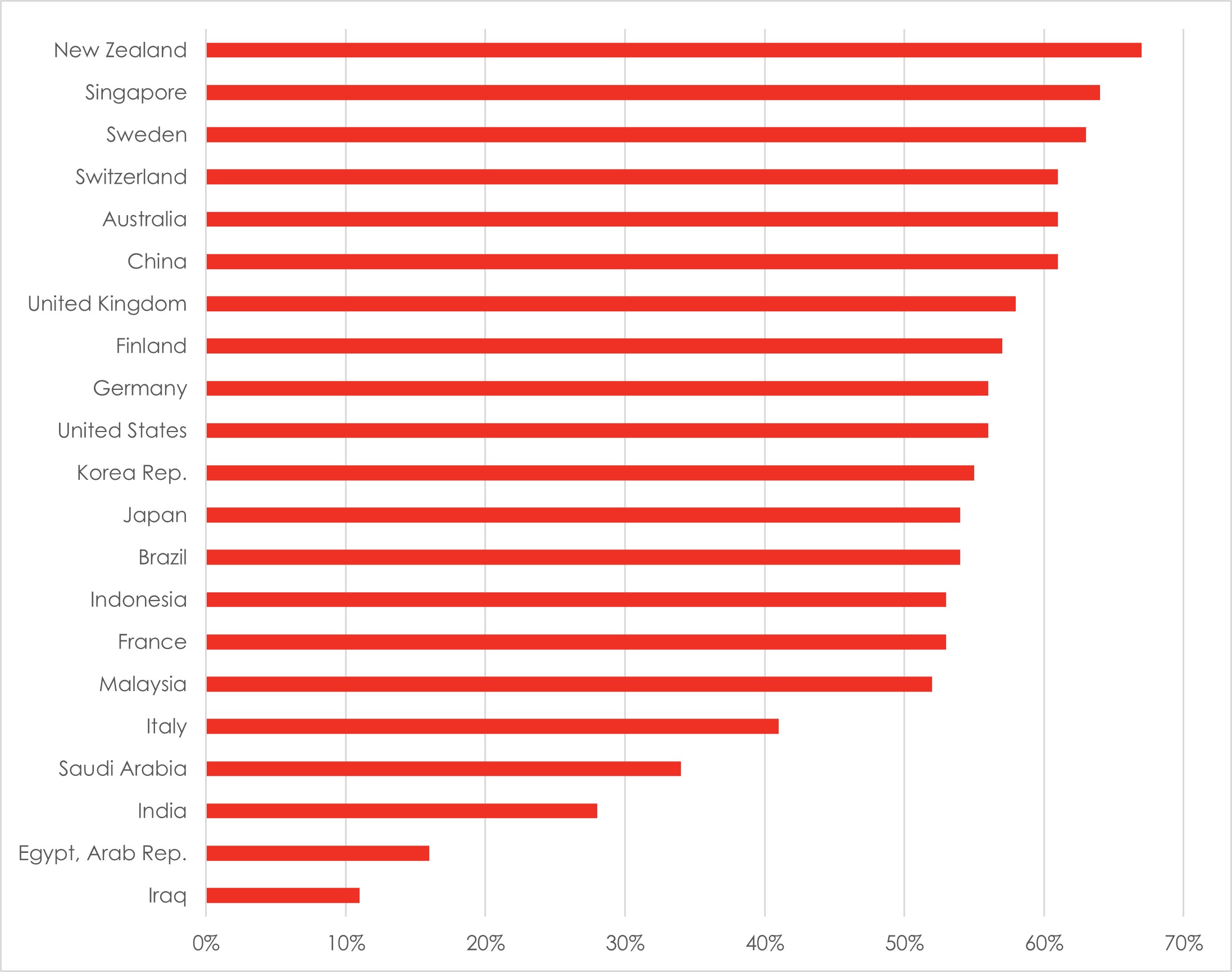
Source: World Bank; Data as of 2022
What is required to support women in the workforce? Some considerations are listed below, though they are by no means exhaustive:
India: Awaiting concrete steps to unlock potential
Female labour participation rates in India have historically been amongst the lowest compared to other major regions. This has been attributed to societal attitudes towards the status of women, and the fact that many women in India perform unpaid work that is not captured by economic measures of formal employment, as previously discussed. Moreover, the rise of industrialisation in India since the turn of the century has resulted in an increase in household incomes, which further reduced women’s employment rates since there may be a less pressing need for them to participate in the labour market.
Exhibit 2: India’s female labour force participation (%) has historically been amongst the lowest globally, but we are starting to see an uptick from 26% to 28% after the pandemic
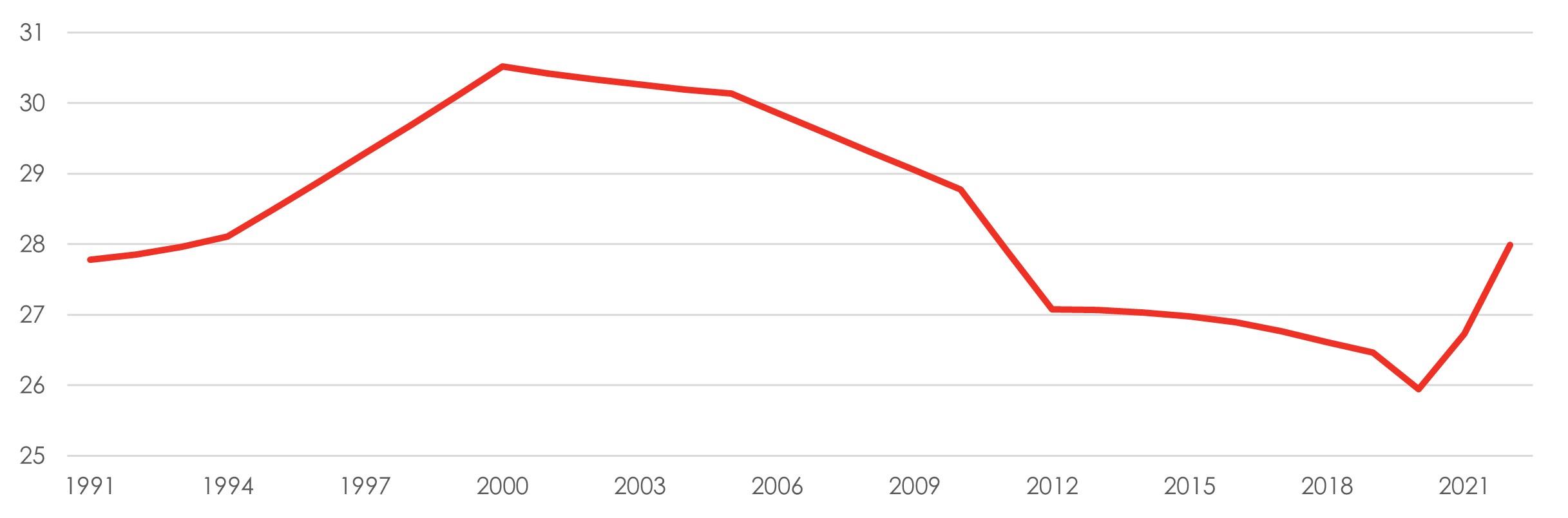
Source: World Bank; Bank of Singapore
Closing the gender gap in employment could expand India’s GDP by close to a third by 205010. We believe that there is significant growth potential if India is able to increase female labour participation rates – though this will be contingent on policy support and reforms, amongst other factors.
Equality for women is good for business
Companies also greatly benefit from increasing employment and leadership opportunities for women, which is shown to increase organizational effectiveness and growth. It is estimated that companies with three or more women in senior management functions score higher in all dimensions of organizational performance11.
Female leaders can set in motion a virtuous cycle by not only implementing workplace policies that promote gender equality (e.g. reducing the pay gap between men and women, and attracting a more diverse workforce), but also by being role models and providing unique mentorship to other women12. Studies have also shown that female leaders help to increase productivity, enhance collaboration, inspire organisational dedication, and improve fairness13.
According to MSCI’s Women on Boards and Beyond 2023 Progress Report14, women held only 25.8% of board seats at large- and mid-cap companies on the MSCI All Country World Index (ACWI), up 1ppt from 2022. The proportion falls to 17.1% in Emerging Markets (EM), and only 14.5% of constituents of the MSCI EM Index have at least 30% of women on boards (MSCI ACWI: 41.2%). Globally, board leadership roles were still dominated by men, with women only occupying 9.1% and 6.5% of chair and chief executive officer (CEO) roles, respectively.
Japan: Shifting from quantity to quality
In Japan, the Abe administration’s “Womenomics” has received mixed reviews. While the Japanese government has pointed out that a significant 3.3m women had joined the workforce between 2012 to 2019, and that the number of women in private sector management positions approached 10% across the same period, other statistics show that in 2017, half of the 28m women in the Japanese labour market were in non-regular jobs with shorter working hours, lower pay, and fewer benefits, compared to just 16.7% of Japan’s 35m male workers. By 2019, these proportions had risen to 56% and 22.8%, respectively15. In 2023, the Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE) also had a female board ratio of only 13%, less than half the average of global peers16. Therefore, while female labour participation in Japan improved in quantity, this is less clear in terms of quality.
Exhibit 3: Japan’s GDP per capita (JPY m) rose as female labour force participation (%) increased, notwithstanding the initial dip in the early 1970s
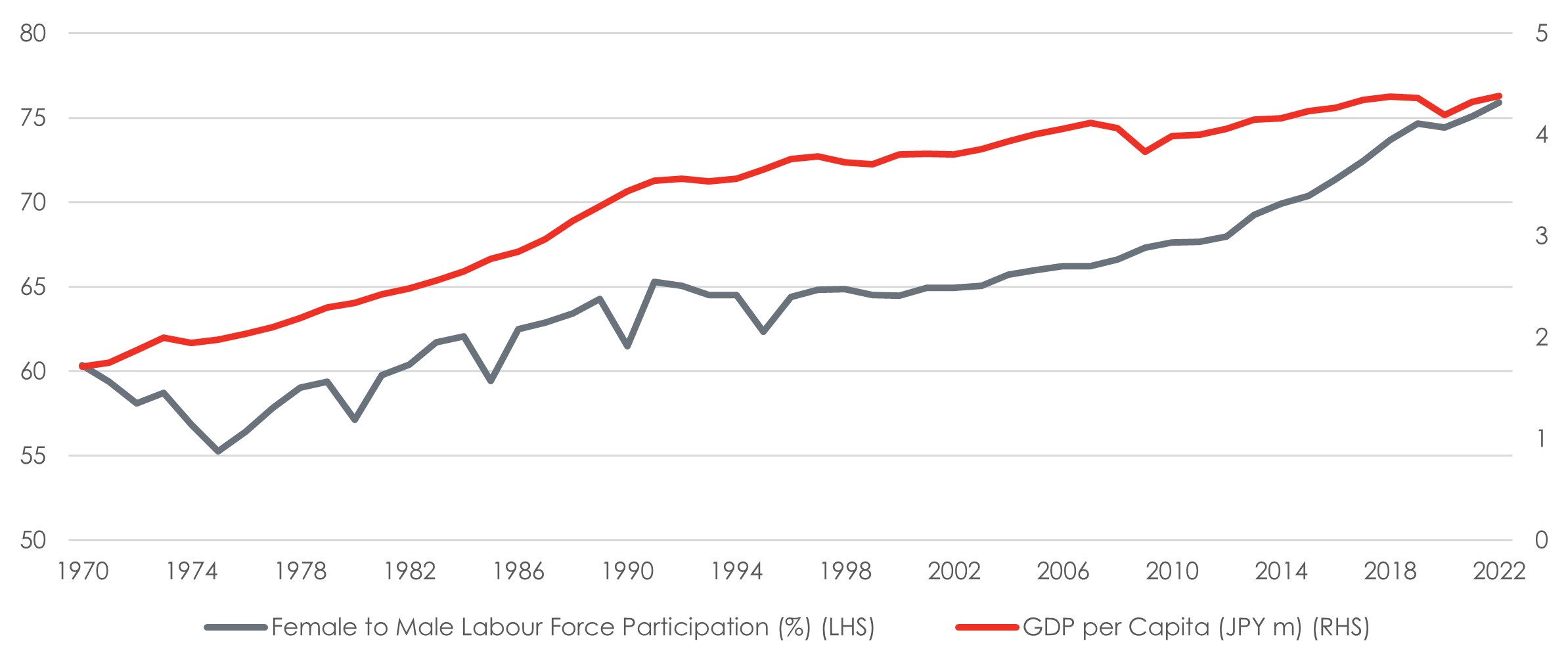
Source: World Bank; Bank of Singapore
Nonetheless, the TSE reforms proposed in March 2023 aim to herald the next era of gender parity. The TSE has set a target of getting women to occupy 30% of executive roles by 2030, with companies listed on the TSE Prime Market Index being urged to fulfil the requirement before 2030. This could help endear more Japanese companies to foreign institutional investors like BlackRock and Goldman Sachs Asset Management, which have committed to vote against Japanese firms with few or no female board members17.
Exhibit 4: Japan lags the G-7 in female board representation and has significant potential to grow
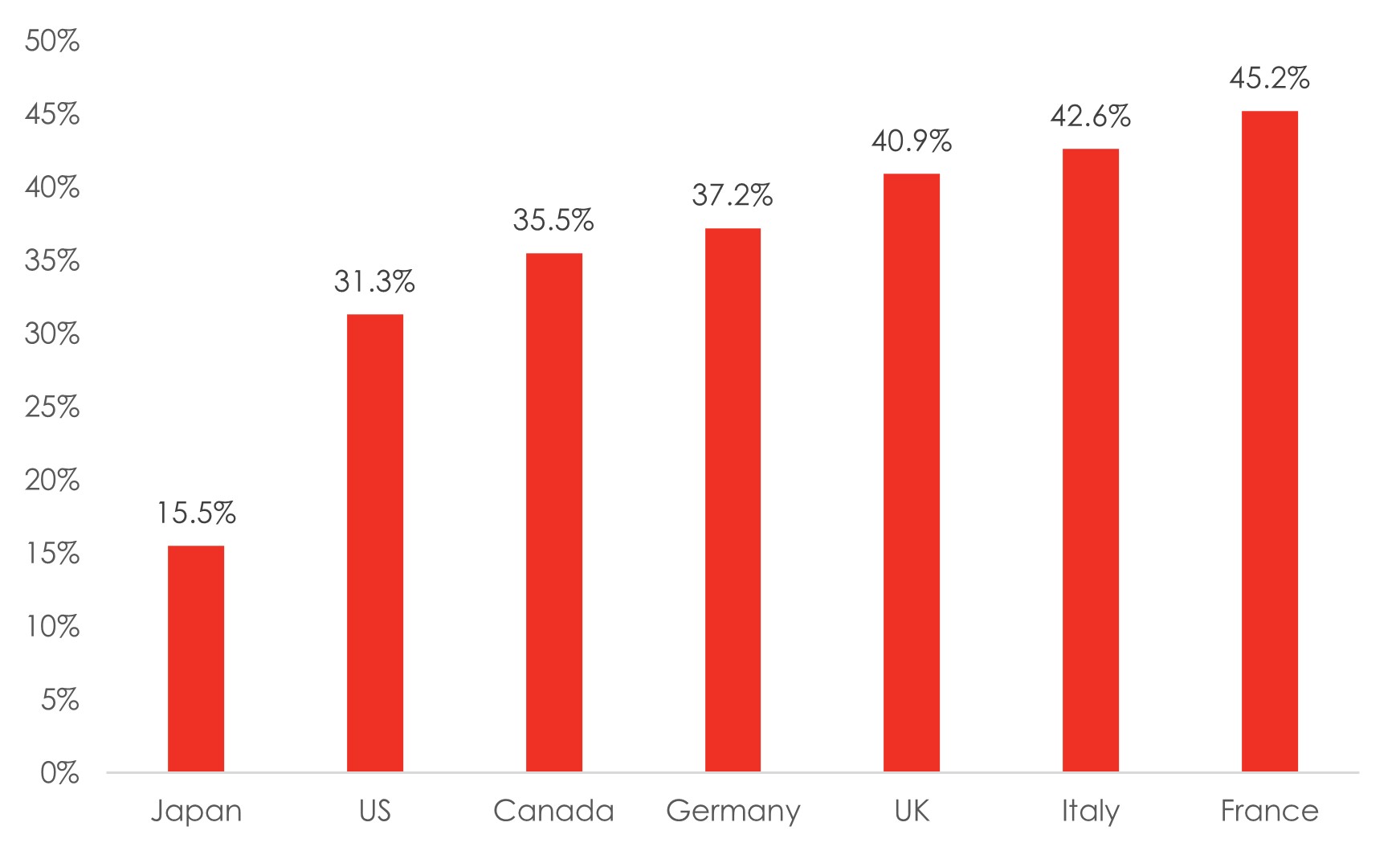
Source: OECD; Bloomberg; Bank of Singapore
Note: Data shows female share of seats on boards of the largest publicly listed companies in each country as of 2022.
Implications for investors
As discussed earlier, closing the gender gap in employment could expand India’s GDP by close to a third by 2050, and there is significant growth potential if India is able to increase female labour participation rates. As for Japan, while female labour participation rates are not low, there is still a gap in terms of gender parity and the next step should be a focus on the “quality” of participation. More benefits for companies and businesses can be reaped, for instance, by raising the percentage of women in management positions, and this is promising from the corporate reforms that are being undertaken by the country. Indeed, Japan’s corporate governance reforms have been cited as one of the catalysts for the market rally since last year. We currently have an Overweight rating on Japan equities, and believe that there is further room for these reforms to play out.
Separately, microfinancing initiatives have gained traction in recent years as a potential solution to uplift women and encourage female economic participation. Microfinancing provides capital and training, often to women living in rural, poverty-stricken regions, so they can engage in income producing activities and even set up small businesses, thereby using their business profits to improve household living conditions. Investors looking to gain exposure to microfinancing could consider impact funds, which could cut across both public and private markets.
2 https://www.pwc.com/gx/en/news-room/press-releases/2020/women-in-work-index-2020.html
3 https://doi.org/10.1787/5jm2hz8dgls6-en
4 https://www.weforum.org/publications/global-gender-gap-report-2023/
5 https://www.oecd.org/dev/development-gender/Unpaid_care_work.pdf
7 https://www.oecd-forum.org/posts/redefining-reality-the-truth-behind-the-unpaid-care-economy
9 https://www.ilo.org/infostories/en-GB/Stories/Employment/barriers-women#intro
12 https://www.rockefellerfoundation.org/wp-content/uploads/Women-in-Leadership-Why-It-Matters.pdf
13 https://www.apa.org/topics/women-girls/female-leaders-make-work-better
Disclaimers and Disclosures
This material is prepared by Bank of Singapore Limited (Co Reg. No.: 197700866R) (the “Bank”) and is distributed in Singapore by the Bank.
This material does not provide individually tailored investment advice. This material has been prepared for and is intended for general circulation. The contents of this material does not take into account the specific investment objectives, investment experience, financial situation, or particular needs of any particular person. You should independently evaluate the contents of this material, and consider the suitability of any product discussed in this material, taking into account your own specific investment objectives, investment experience, financial situation and particular needs. If in doubt about the contents of this material or the suitability of any product discussed in this material, you should obtain independent financial advice from your own financial or other professional advisers, taking into account your specific investment objectives, investment experience, financial situation and particular needs, before making a commitment to purchase any product.
The Bank shall not be responsible or liable for any loss (whether direct, indirect or consequential) that may arise from, or in connection with, any use of or reliance on any information contained in or derived from this material, or any omission from this material, other than where such loss is caused solely by the Bank’s wilful default or gross negligence.
This material is not and should not be construed, by itself, as an offer or a solicitation to deal in any product or to enter into any legal relations. You should contact your own licensed representative directly if you are interested in buying or selling any product discussed in this material.
This material is not intended for distribution, publication or use by any person in any jurisdiction outside Singapore, Hong Kong or such other jurisdiction as the Bank may determine in its absolute discretion, where such distribution, publication or use would be contrary to applicable law or would subject the Bank or its related corporations, connected persons, associated persons or affiliates (collectively “Affiliates”) to any licensing, registration or other requirements in such jurisdiction.
The Bank and its Affiliates may have issued other reports, analyses, or other documents expressing views different from the contents of this material, and may provide other advice or make investment decisions that are contrary to the views expressed in this material, and all views expressed in all reports, analyses and documents are subject to change without notice. The Bank and its Affiliates reserve the right to act upon or use the contents of this material at any time, including before its publication.
The author of this material may have discussed the information or views contained in this material with others within or outside the Bank, and the author or such other Bank employees may have already acted on the basis of such information or views (including communicating such information or views to other customers of the Bank).
The Bank, its employees (including those with whom the author may have consulted in the preparation of this material))and discretionary accounts managed by the Bank may have long or short positions (including positions that may be different from or opposing to the views in this material or may be otherwise interested in any of the product(s) (including derivatives thereof) discussed in material, may have acquired such positions at prices and market conditions that are no longer available, may from time to time deal in such product(s) and may have interests different from or adverse to your interests.
Analyst Declaration
The analyst(s) who prepared this material certifies that the opinions contained herein accurately and exclusively reflect his or her views about the securities of the company(ies) and that he or she has taken reasonable care to maintain independence and objectivity in respect of the opinions herein.
The analyst(s) who prepared this material and his/her associates [have / do not] have financial interests in the company(ies). Financial interests refer to investments in securities, warrants and/or other derivatives. The analyst(s) receives compensation based on the overall revenues of Bank of Singapore Limited, and no part of his or her compensation was, is, or will be directly or indirectly related to the inclusion of specific recommendations or views in this material. The reporting line of the analyst(s) is separate from and independent of the business solicitation or marketing departments of Bank of Singapore Limited.
The analyst(s) and his/her associates confirm that they do not serve as directors or officers of the company(ies) and the company(ies)or other third parties have not provided or agreed to provide any compensation or other benefits to the analyst(s) in connection with this material.
An “associate” is defined as (i) the spouse, parent or step-parent, or any minor child (natural or adopted) or minor step-child, or any sibling or step-sibling of the analyst; (ii) the trustee of a trust of which the analyst, his spouse, parent or step-parent, minor child (natural or adopted) or minor step-child, or sibling or step-sibling is a beneficiary or discretionary object; or (iii) another person accustomed or obliged to act in accordance with the directions or instructions of the analyst.
Conflict of Interest Declaration
The Bank is a licensed bank regulated by the Monetary Authority of Singapore in Singapore. Bank of Singapore Limited, Hong Kong Branch (incorporated in Singapore with limited liability), is an Authorized Institution as defined in the Banking Ordinance of Hong Kong (Cap 155), regulated by the Hong Kong Monetary Authority in Hong Kong and a Registered Institution as defined in the Securities and Futures Ordinance of Hong Kong (Cap.571) regulated by the Securities and Futures Commission in Hong Kong. The Bank, its employees and discretionary accounts managed by its Singapore Office/Hong Kong Office may have long or short positions or may be otherwise interested in any of the investment products (including derivatives thereof) referred to in this document and may from time to time dispose of any such investment products. The Bank forms part of the OCBC Group (being for this purpose Oversea-Chinese Banking Corporation Limited (“OCBC Bank”) and its subsidiaries, related and affiliated companies). OCBC Group, their respective directors and/or employees (collectively “Related Persons”) may have interests in the investment products or the issuers mentioned herein. Such interests include effecting transactions in such investment products, and providing broking, investment banking and other financial services to such issuers. OCBC Group and its Related Persons may also be related to, and receive fees from, providers of such investment products. There may be conflicts of interest between OCBC Bank, the Bank, OCBC Investment Research Private Limited, OCBC Securities Private Limited or other members of the OCBC Group and any of the persons or entities mentioned in this report of which the Bank and its analyst(s) are not aware due to OCBC Bank’s Chinese Wall arrangement.
The Bank adheres to a group policy (as revised and updated from time to time) that provides how entities in the OCBC Group manage or eliminate any actual or potential conflicts of interest which may impact the impartiality of research reports issued by any research analyst in the OCBC Group.
Other Disclosures
Singapore
Where this material relates to structured deposits, this clause applies:
The product is a structured deposit. Structured deposits are not insured by the Singapore Deposit Insurance Corporation. Unlike traditional deposits, structured deposits have an investment element and returns may vary. You may wish to seek independent advice from a financial adviser before making a commitment to purchase this product. In the event that you choose not to seek independent advice from a financial adviser, you should carefully consider whether this product is suitable for you.
Where this material relates to dual currency investments, this clause applies:
The product is a dual currency investment. A dual currency investment product (“DCI”) is a derivative product or structured product with derivatives embedded in it. A DCI involves a currency option which confers on the deposit-taking institution the right to repay the principal sum at maturity in either the base or alternate currency. Part or all of the interest earned on this investment represents the premium on this option.
By purchasing this DCI, you are giving the issuer of this product the right to repay you at a future date in an alternate currency that is different from the currency in which your initial investment was made, regardless of whether you wish to be repaid in this currency at that time. DCIs are subject to foreign exchange fluctuations which may affect the return of your investment. Exchange controls may also be applicable to the currencies your investment is linked to. You may incur a loss on your principal sum in comparison with the base amount initially invested. You may wish to seek advice from a financial adviser before making a commitment to purchase this product. In the event that you choose not to seek advice from a financial adviser, you should carefully consider whether this product is suitable for you.
Hong Kong
This material has not been delivered for registration to the Registrar of Companies in Hong Kong and its contents have not been reviewed by any regulatory authority in Hong Kong. Accordingly: (i) the shares/notes may not be offered or sold in Hong Kong by means of any document other than to persons who are "Professional Investors" within the meaning of the Securities and Futures Ordinance (Cap. 571) of Hong Kong and the Securities and Futures (Professional Investor) Rules made thereunder or in other circumstances which do not result in the document being a "prospectus" within the meaning of the Companies (Winding Up and Miscellaneous Provisions) Ordinance (Cap. 32) of Hong Kong or which do not constitute an offer to the public within the meaning of the Companies (Winding Up and Miscellaneous Provisions) Ordinance; and (ii) no person may issue any invitation, advertisement or other material relating to the shares/notes whether in Hong Kong or elsewhere, which is directed at, or the contents of which are likely to be accessed or read by, the public in Hong Kong (except if permitted to do so under the securities laws of Hong Kong) other than with respect to the shares/notes which are or are intended to be disposed of only to persons outside Hong Kong or only to "Professional Investors" within the meaning of the Securities and Futures Ordinance and the Securities and Futures (Professional Investor) Rules made thereunder.
Where this material involves derivatives, do not invest in it unless you fully understand and are willing to assume the risks associated with it. If you have any doubt, you should seek independent professional financial, tax and/or legal advice as you deem necessary.
Where this material relates to a Complex Product, this clause applies:
Warning Statement and Information about Complex Product
(Applicable to accounts managed by Hong Kong Relationship Manager)
Where this material relates to a Complex Product – funds and ETFs, this clause applies additionally:
Where this material relates to a Complex Product (Options and its variants, Swap and its variants, Accumulator and its variants, Reverse Accumulator and its variants, Forwards), this clause applies additionally:
Where this material relates to a Loss Absorption Product, this clause applies:
Warning Statement and Information about Loss Absorption Products
(Applicable to accounts managed by Hong Kong Relationship Manager)
Before you invest in any Loss Absorption Product (as defined by the Hong Kong Monetary Authority), please read and ensure that you understand the features of a Loss Absorption Product, which may generally have the following features:
Where this material relates to a certificate of deposit, this clause applies:
It is not a protected deposit and is not protected by the Deposit Protection Scheme in Hong Kong.
Where this material relates to a structured deposit, this clause applies:
It is not a protected deposit and is not protected by the Deposit Protection Scheme in Hong Kong.
Where this material relates to a structured product, this clause applies:
This is a structured product which involves derivatives. Do not invest in it unless you fully understand and are willing to assume the risks associated with it. If you are in any doubt about the risks involved in the product, you may clarify with the intermediary or seek independent professional advice.
Dubai International Financial Center
Where this material relates to structured products and bonds, this clause applies:
The Distributor represents and agrees that it has not offered and will not offer the product to any person in the Dubai International Financial Centre unless such offer is an “Exempt Offer” in accordance with the Market Rules of the Dubai Financial Services Authority (the “DFSA”).
The DFSA has no responsibility for reviewing or verifying any documents in connection with Exempt Offers.
The DFSA has not approved the Information Memorandum or taken steps to verify the information set out in it, and has no responsibility for it.
The product to which this document relates may be illiquid and/or subject to restrictions in respect of their resale. Prospective purchasers of the products offered should conduct their own due diligence on the products.
Please make sure that you understand the contents of the relevant offering documents (including but not limited to the Information Memorandum or Offering Circular) and the terms set out in this document. If you do not understand the contents of the relevant offering documents and the terms set out in this document, you should consult an authorised financial adviser as you deem necessary, before you decide whether or not to invest.
Where this material relates to a fund, this clause applies:
This Fund is not subject to any form of regulation or approval by the Dubai Financial Services Authority (“DFSA”). The DFSA has no responsibility for reviewing or verifying any Prospectus or other documents in connection with this Fund. Accordingly, the DFSA has not approved the Prospectus or any other associated documents nor taken any steps to verify the information set out in the Prospectus, and has no responsibility for it. The Units to which this Fund relates may be illiquid and/or subject to restrictions on their resale. Prospective purchasers should conduct their own due diligence on the Units. If you do not understand the contents of this document you should consult an authorized financial adviser. Please note that this offer is intended for only Professional Clients and is not directed at Retail Clients.
These are also available for inspection, during normal business hours, at the following location:
Bank of Singapore
Office 30-34 Level 28
Central Park Tower
DIFC, Dubai
U.A.E
BOS Wealth Management Europe S.A., UK Branch
BOS Wealth Management Europe S.A., UK Branch (BOSWME UK), is authorized and regulated by the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) and is providing this material for informational purposes only. BOSWME UK does not endorse any specific investments or financial products mentioned in this material. BOSWME UK and its employees accept no liability for any loss or damage arising from the use of this material or reliance on its content.
This material is being distributed to and is directed only at persons in the UK who meet the requirements to be considered “Professional Clients” within the meaning of the Conduct of Business Sourcebook rules on client categorisation, part of the FCA Handbook (the “FCA Rules”) and is not intended for retail investors.
Any person in the UK who receives this material will be deemed to have represented and agreed that it can be considered a Professional Client. Any such recipient will also be deemed to have represented and agreed that it has not received this material on behalf of persons in the UK other than Professional Clients for whom the investor has authority to make decisions on a wholly discretionary basis. BOSWME UK will rely upon the truth and accuracy of the foregoing representations and agreements. Any person who is not a Professional Client should not act or rely on this material or any of their contents.
Investing in financial markets carries the risk of losing capital, and investors should be aware of and carefully consider this risk before making any investment decisions. The value of investments can fluctuate, and there is no guarantee that investors will recoup their initial investment. Past performance is not indicative of future results, and the performance of investments can be affected by various factors, including but not limited to market conditions, economic factors, and changes in regulations or tax laws. Forward-looking statements should not be considered as guarantees or predictions of future events. Investors should be prepared for the possibility of losing all or a portion of their invested capital. It is recommended that investors seek professional advice and conduct thorough research before making any investment decisions.
Cross Border Disclaimer and Disclosures
Refer to https://www.bankofsingapore.com/Disclaimers_and_Disclosures.html for cross-border marketing disclaimers and disclosures.
